Best practices per l’installazione di un Milestone XProtect Recording Server fisico su server DELL PowerEdge R7425
Dal momento che un Milestone XProtect Recording Server può beneficiare della Hardware acceleration come descritto in XProtect VMS 2018 R2 – Hardware acceleration (explained) e nell’ XProtect VMS 2019 R3 – Hardware acceleration (explained):
“The recording server is now using GPU resources if they are available. This will reduce the CPU load during video motion analysis and improve the general performance of the recording server.
Hardware accelerated video motion detection uses GPU resources on:
- Intel CPUs that support Intel Quick Sync.
- NVIDIA® display adapters connected to your recording server.”
Di conseguenza può essere più semplice utilizzare Recording Server fisici anziché virtuali, di seguito riporto alcune best practices per l’installazione di un Milestone XProtect Recording Server fisico su server DELL PowerEdge R7425 basandosi sulle indicazioni riportate nell’articolo How to set up the XProtect Recording Server for best performance.
La configurazione del Raid per il drive su cui verranno salvate le registrazioni deve essere fatta tenendo presente delle seguenti indicazioni:
“Configure the recording and archive hard drives to have a cluster size (block size) of 64K or higher.”
“Ensure RAID stripe size is set to 512K or higher.”
Analoghe considerazioni sono riportate nell’XProtect VMS 2019 R3 – Configure storage:
“If you will be using RAID on your storage system, make sure it is set to a RAID stripe of 512kB or larger. Using a smaller block size may result in not getting the optimal performance out of the RAID system.
By default, Windows formats an NTFS disk with a 4 kB block size. For best performance, make sure your storage is formatted with NTFS 64 kB block size, regardless of the use of RAID and JBOD.
If you will be recording to a storage system running RAID 5 or RAID 6, you should take particular care to ensure the storage system has sufficient performance to meet the worst-case scenario of recording and playback while the RAID is recovering from a disk failure (rebuilding the RAID).”
Altre utili indicazioni sono riportante nella White Paper XProtect Storage Architecture and Recommendations:
“RAID 10 provides the best performance and redundancy and is often called ‘the best RAID configuration for mission critical applications and databases’. In an XProtect VMS RAID 10 is especially good for the recording database – whether or not archiving is used.
However, the benefits of RAID 10 though come at the cost of needing a lot of hard disks making this configuration quite costly – especially when needing a lot of disk space as the XProtect VMS often requires.
This means that, for larger XProtect VMS systems with many cameras per recording server storing recordings for a longer period, RAID 10 may become too expensive. In this case a combination of a smaller RAID 10 array for the recording database, and a larger RAID 5 or 6 array for an archive database could be a more cost-efficient solution.”
“Apart from the most used RAID configurations covered here, there are some additional RAID configurations called RAID 50, RAID 60 and RAID 100, which can offer some specific benefits.”
“recording many devices in parallel and in real-time to the recording databases causes a lot of non-sequential writing on the disks and storage system. Designing a storage system that is fast enough to handle this and large enough to store the recordings for the required time can be expensive, which is where archiving can be used to reduce the cost without compromising on performance”
Configurazione dei Virtual Disks
Dalle indicazioni precedenti e consigliabile configurare lo storage su cui sono salvate le registrazioni con Stripe Size a 512K e il volume formattato con dimensioni unità di allocazione a 64k come segue, per quanto riguarda il livello di RAID dovrebbe essere utilizzato un RAID 10 o un RAID 50 se lo spazio risultante non è sufficiente (si tenga conto che la registrazione implica principalmente scritture non sequenziali):
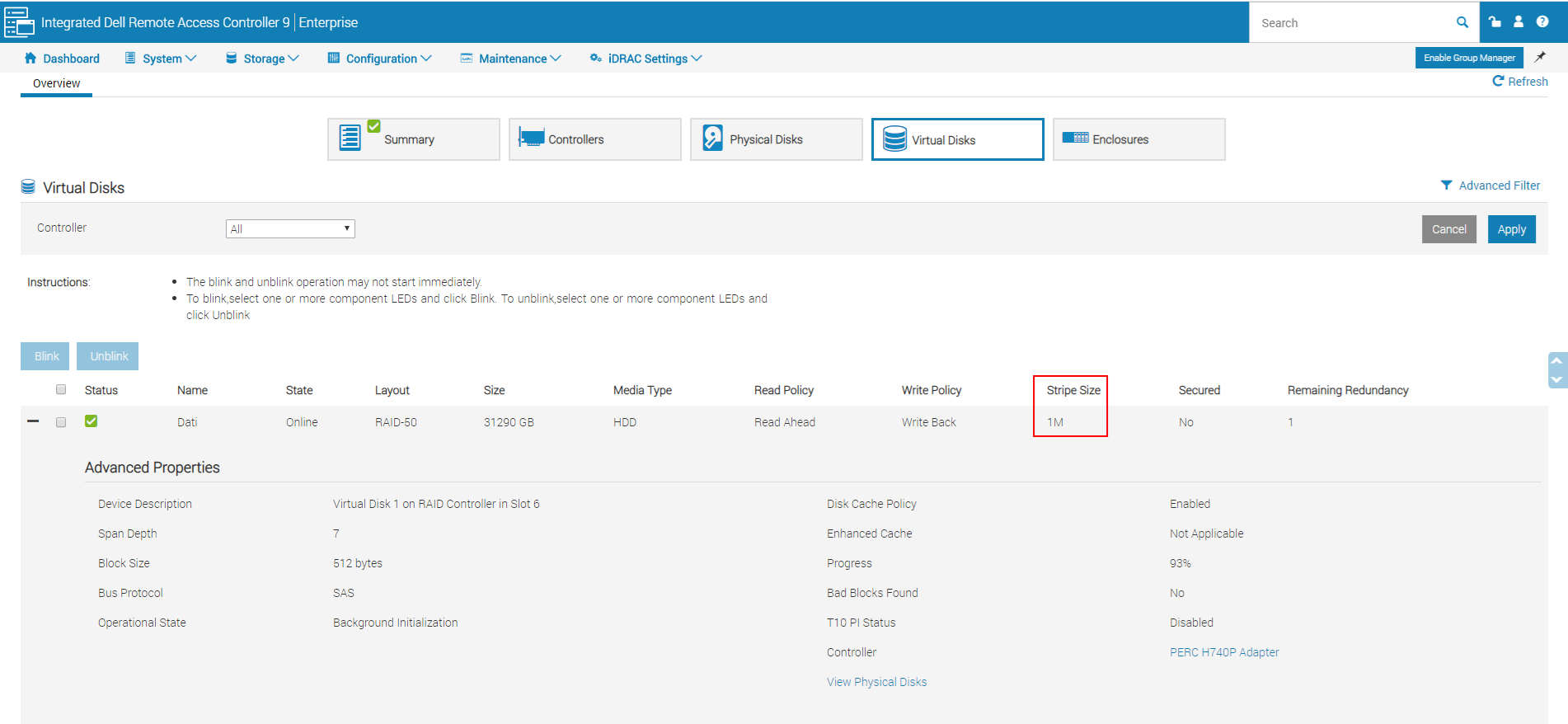
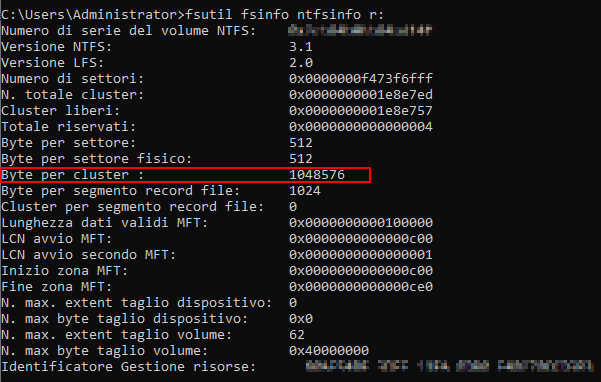
Nella scelta del tipo di Raid occore tenere presente che DELL sconsiglia l’uso del RAID 5 e del RAID 50 con dischi di dimensione di 2 TB o superiori (a riguardo si veda Considerazioni per la scelta del RAID corretto), mentre l’utilizzo del RAID 6 o 60 potrebbe avere performance non sufficienti le scritture non sequenziali, quindi se possibile è meglio utilizzare il RAID 10.
Per quanto riguarda il disco di sistema dal momento che durante l’installazione viene formattato con dimensioni unità di allocazione 4kb conviene configurare il Raid con uno stripe size di 64k per avere un buon connubio tra performance e spazio occupato (a riguardo si vedano anche le considerazioni fatte nel mio post SQL Server e il Disk Partition Alignment)
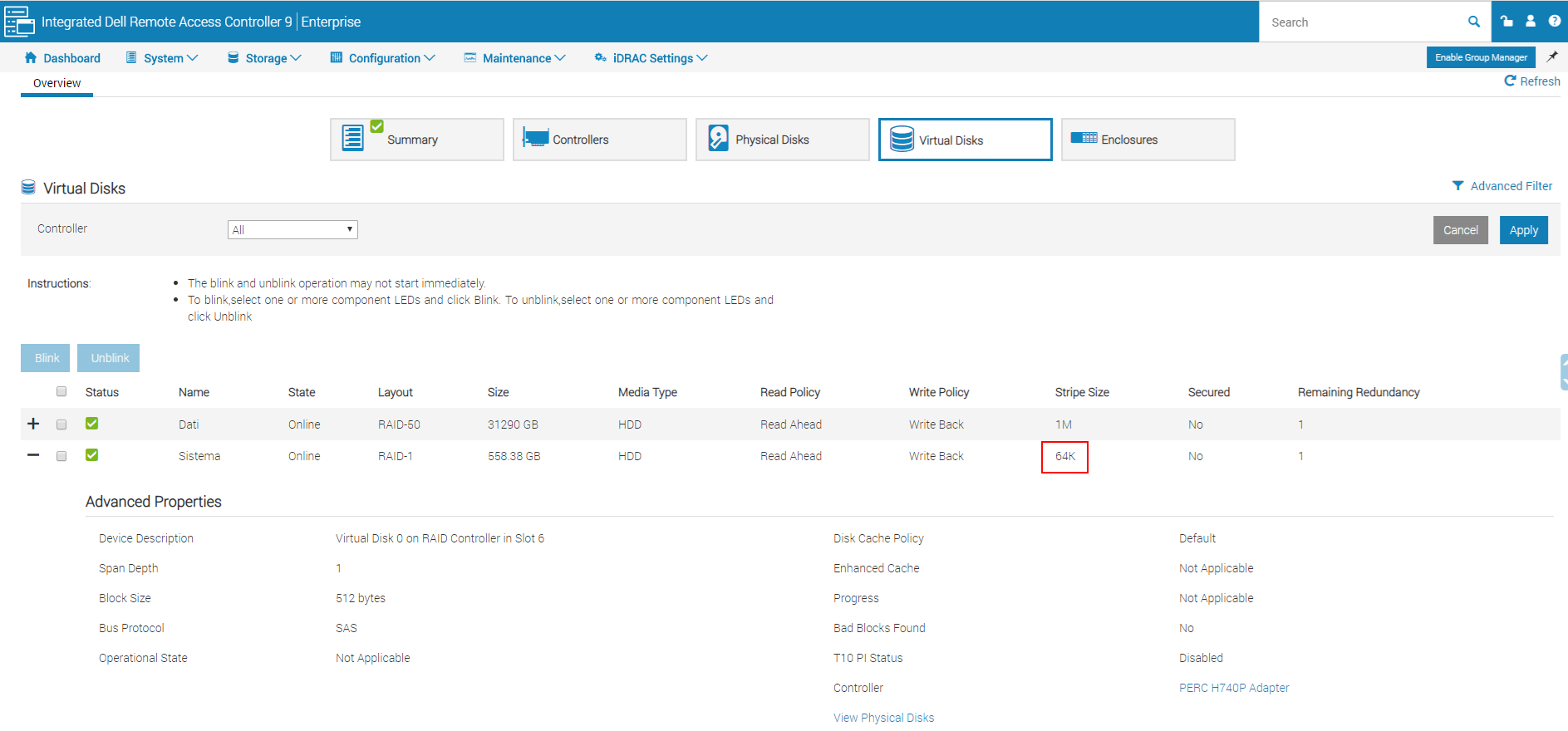
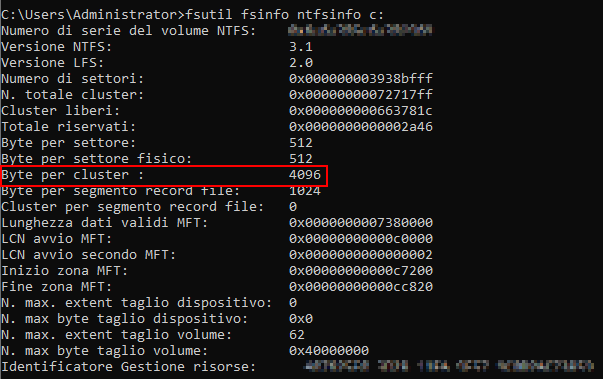
Configurazione da eseguire sul volume su cui vengono salvate le registrazioni
Come indicato in How to set up the XProtect Recording Server for best performance e in XProtect Storage Architecture and Recommendations occorre tenere presenti le seguenti:
“‘Windows Search Indexing’ can impact recording performance when it indexes the media database files. Therefore, it is recommended to either disable ‘Windows Search Indexing’ or change its configuration so it does not index the drives storing the XProtect VMS media database files.”
“‘Windows Disk Defragmenter’ can impact recording performance when it defragments the disks. Therefore, it is recommended to configure ‘Windows Disk Defragmenter’ so it doesn’t defragment the disks storing the XProtect VMS media database files. The XProtect VMS itself will ensure that all database files are written so they are not fragmented.”
“The virus scanner on the XProtect VMS recording server may interfere with recording performance as it scans the data and files being written to disk.
To prevent this, certain folders and file types must be excluded from the scan.
For detailed information on how to properly configure the virus scanner, please refer to the ‘XProtect VMS – Administrator manual’ which can be found here: https://www.milestonesys.com/support/help-yourself/manuals-and-guides/?prod=3&type=13&lang=27“
“Disable real-time antivirus scanning; instead choose to scan the system based on a schedule. Consult the XProtect Administrator’s Manual regarding which files/folders and processes to exclude. You can also find more information about anti-virus scanning and XProtect in KB 1004, “Configure anti-virus software on XProtect systems (best practices).””
“Configure your maximum recording and archive retention limits so that video is deleted upon a set schedule, and not when the hard disk drive reaches its maximum capacity. For best performance, we recommend to maintain at least 15% of the drive free .”
“If your surveillance server storage has one single storage array, do not archive. (See the corresponding KB 3614, “When should I archive?”)”
“Disable any non-essential Windows tasks and processes that affect the file system. These could include the indexing service and the volume shadow copy service. Also make sure to never use Windows drive compression as it will slow down all write-to-disk operations.”
Quindi sul volume su cui vengono salvate le registrazioni occorre
- Disabilitare l’indicizzazione e ogni Windows tasks non essenziale che può rallentare le opeazioni su disco
- Evitare che venga eseguita la deframmentazione
- Gestirle le esclusioni dell’antivirus come indicato in XProtect VMS 2019 R3 – Virus scanning exclusions (explained) e in Configure anti-virus software on XProtect systems (best practices)
- Assicurarsi di avere sul volume almeno il 15% di spazio libero
- Evitare di creare l’archiviazione sullo stesso storage array utilizzato per le registrazioni
Installazione driver, firmware e tool DELL
Per l’installazione di driver e firmware è possibile utilizzare il tool Dell EMC repository Manager (DRM), attualmente alla versione 3.3, tramite cui è possibile creare un’iso per l’installazione e/o l’aggiornamento di Driver, Bios e Firmware.
Inoltre per una più semplice gestione del server è consigliabile installare anche i seguenti:
XProtect Corporate How to install the recording server
Per ulteriori informazioni si vedano anche i seguenti

[…] avevo scritto nel post Best practices per l’installazione di un Milestone XProtect Recording Server fisico su server … un Milestone XProtect Recording Server può beneficiare della Hardware acceleration come descritto […]
[…] di un numero opportuno di unità di memorizzazione configurate in RAID 10 (a riguardo si veda Best practices per l’installazione di un Milestone XProtect Recording Server fisico su server DELL…). Ne consegue che utilizzare SSD in server di registrazione Milestone implicherebbe una maggiore […]
[…] trattato il tema del Disk Partion Alignement nei post SQL Server e il Disk Partition Alignment, Best practices per l’installazione di un Milestone XProtect Recording Server fisico su server DELL… e Configurazione del block storage di Veeam, ma in questo post mi concentrerò sul Disk Partion […]
[…] abbia già trattato in parte questo tema nel post Best practices per l’installazione di un Milestone XProtect Recording Server fisico su server DELL… di seguito mi focalizzerò maggiormente sugli aspetti legati allo […]