Autenticazione NTLM alcune note
L’autenticazione NTLM è nota anche come autenticazione integrata di Windows e viene utilizzato come protocollo di autenticazione per le transazioni tra due computer nel seguenti casi:
- Client Windows 2000 o Windows XP Professional che si autenticano in un dominio Windows NT 4.0.
- Client Windows NT 4.0 Workstation che ottiene che si autentica in un dominio AD.
- Client Windows NT 4.0 Workstation che si autentica in un dominio Windows NT 4.0.
- Utenti di un dominio Windows NT 4.0 che si autenticano in un dominio AD.
- Un client su cui è in esecuzione Windows 95, Windows 98 o Windows Millennium Edition che sta eseguendo l’autenticazione in un controller di dominio.
- Computer che non fanno parte di un dominio, quali i server e i gruppi di lavoro autonomi.
- Membri non di dominio quando si autenticano a membri di domino
- Accesso a share quando si utilizza l’indirizzo IP (per esempio \\192.168.1.100\share)
Microsoft ha sviluppato un miglioramento per NTLM, denominato NTLM versione 2, che migliora significativamente i meccanismi di autenticazione e protezione di sessione. NTLM 2 è disponibile per Windows NT 4.0 SP4 ed è supportato a livello nativo a partire da Windows 2000. È possibile aggiungere il supporto per NTLM 2 a Windows 98 installando le estensioni client di Active Directory.
Una volta aggiornati tutti i computer basati su Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 98 Seconda Edizione e Windows NT 4.0, è possibile migliorare notevolmente la protezione della propria azienda configurando client, server e controller di dominio affinché utilizzino esclusivamente NTLM 2 (non LM o NTLM).
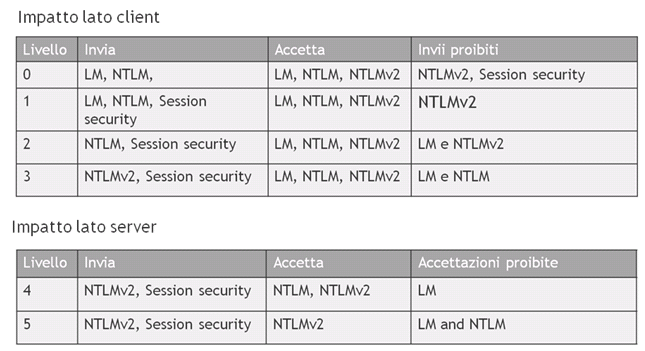
L’autenticazione NTLM si configura con la chiave HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA\LMCompatibilityLevel
· 0 =Send LAN Manager (LM) responses and NTLM responses.
Client computers send LM responses and NTLM responses. Client computers never use NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers accept LM authentication, NTLM authentication, and NTLMv2 authentication.
(Default per Windows XP e Windows 2000)
· 1 Send LM authentication and NTLM authentication and use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated.
Client computers use LM authentication and NTLM authentication. Client computers use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers accept LM authentication, NTLM authentication, and NTLMv2 authentication.
· 2 Send only NTLM responses.
Client computers use only NTLM authentication. Client computers use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers accept LM authentication, NTLM authentication, and NTLMv2 authentication.
(Default per Windows server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2)
· 3 Send only NTLMv2 responses.
Client computers use only NTLMv2 authentication. Client computers use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers accept LM authentication, NTLM authentication, and NTLMv2 authentication.
(Default per Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2)
· 4 Send only NTLM responses and refuse LM authentication.
Client computers use only NTLM authentication. Client computers use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers refuse LM authentication. Domain controllers accept NTLM authentication and NTLMv2 authentication.
· 5 Send only NTLMv2 responses and refuse LM authentication and NTLM authentication.
Client computers use only NTLMv2 authentication. Client computers use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers refuse LM authentication and NTLM authentication. Domain controllers accept only NTLMv2 authentication
Per ulteriori informazioni si vedano: