Controller di dominio e Autoenrollment dei certificati
La funzionalità di Autoenrollment dei certificati permette di configurare dei soggetti a cui automaticamente rilasciare i certificati richiesti.
L’Autoenrollment per i certificati computer è stato introdotto in Windows 2000 Server ed è poi stato esteso a tutti i tipi di certificati in Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition.
L’Autoenrollment richiede la versione 2 o 3 dei templates e quindi richiede una enterprise CA installata su un computer con Windows Server 2003 Enterprise o Datacenter, Windows Server 2008 Enterprise, Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard o Datacenter, Windows Server 2012/R2 Standard o Datacenter, Windows Server 2016 Standard o Datacenter.
Di seguito la matrice di supporto dei Certificate Templates:
- Windows 2000 Server: V1
- Windows 2003 Standard: V1
- Windows Server 2003 Enterprise o Datacenter: V1, V2
- Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition: V1
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise o Datacenter: V1, V2, V3
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Foundation, Enterprise, Datacenter: V1, V2, V3
- Windows Server 2012 Standard o Datacenter: V1, V2, V3, V4
L’Autoenrollment non è attivo per default, ma deve essere configurato e tale configurazione è una best practices, a riguardo si veda appunto la best practice AD CS: Computer autoenrollment should be enabled when an enterprise CA is installed:
“An enterprise CA provides autoenrollment features that enable certificates to be issued without user interaction. The autoenrollment operations on client computers and CAs are controlled by Group Policy settings and certificate template settings. Several default certificate templates are enabled for autoenrollment during CA installation. However, Group Policy settings must be enabled by an administrator before client computers can initiate autoenrollment.”
I Domain Controller hanno la prerogativa di ricevere automaticamente Domain Controller Certificate se nella foresta è disponibile una CA Enteprise anche se non è stata configurata una Group Policy per l’Autoenrollment, a riguardo si vedano:
Processing Domain Controller Certificates (in Windows Server 2003/2003 R2 Retired Content)
Windows 2000 Enterprise CA
Unfortunately, domain controller certificates cannot be issued manually from a Windows 2000 enterprise CA for the following
reasons.
A Windows 2000 CA supports only hard-coded certificate templates so that you cannot duplicate and customize the
default certificate template. If the original domain controller certificate was manipulated, it would affect all other domain
controllers that are able to connect to the CA and use auto-enrollment to request certificates.
A Windows Server 2000 CA issues certificates immediately without pending. Since the submission interface on the CA
has limited functionality in Windows 2000 and, therefore, certificate manipulation is required in a pending state, support
for offline domain controllers is particularly problematic.
Therefore, if support for offline certificate request processing is required, it is recommended that you install a Windows 2000
stand-alone CA or a Windows Server 2003 CA.
Issuing Domain Controller Certificates with a Windows Server 2003 CA
A Windows Server 2003 enterprise CA may support V2 templates and pending requests on a per template basis, as well as
support for submitting request attributes in enrollment request from both enterprise and stand-alone CAs. Therefore, the
following sections document the unique procedures for each CA type. V2 templates are only available if the CA was installed
on Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition.
A riguardo si veda anche l’articolo Windows Server 2003 PKI Certificate Autoenrollment:
Every Windows 2003 and Win2K domain controller (DC) automatically receives a DC certificate when the machine joins a domain in which an enterprise CA is defined.
Per maggiori dettagli si veda poi il post Active Directory Domain Controllers and certificate auto-enrollment di Morgan Simonsen (MVP Enterprise Mobility) dove riporta:
All domain controllers are hard coded to automatically enroll for a certificate based on the Domain Controller template if it is available for enrollment at a certificate authority in the forest. Hard coded in this case means it is in the code, it is not configured in any local or domain based policy. This is one of the few cases where Windows will auto-enroll for a certificate without auto-enrollment being configured in Group Policy.
Questo significa che se viene installata una Enterprise CA di conseguenza verranno registrati nella foresta Active Directory i certificate template e quindi Domain Controller eseguiranno richieste per l’autoenrollment di certificati.
E’ possibile vedere i certificate templates registrati tramite lo snap-in MMC Directory Sites and Services (dssites.msc) analizzando il container Services\Public Key Services\OID oppure tramite il comando:
certutil –CATemplate
Se i Domain Controller non riescono ad ottenere i certificati richiesti tramite autoenrollment verranno registrati sui DC ogni 8 ore eventi di warning e/o di errore nel log Application come ad esempio i seguenti (ma si tenga presente che gli eventi possono essere diversi in base alla ragione che impedisce all’autoenrollment di funzionare):
Event ID: 53
Source: Microsoft-Windows-CertificationAuthority
Level: Warning
Description: Certificate Services denied request RequestNumber because The request subject name is invalid or too long. 0x80094001 (-2146877439). The request was for DCName. Additional information: Error Constructing or Publishing Certificate
(a riguardo si veda Event ID 53 — AD CS Certificate Request (Enrollment) Processing)
Event ID: 6
Source: Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServicesClient-AutoEnrollment
Level: Error
Description: Automatic certificate enrollment for local system failed (0x80094001). The request subject name is invalid or too long.
I motivi possono essere svariati a partire da quelli legati a motivi di rete o infrastrutturali come descritto nella KB310461 Problems occur when the Autoenrollment feature cannot reach an Active Directory domain controller:
This problem may occur if the Autoenrollment feature cannot reach an Active Directory domain controller. In a Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 domain, Active Directory is not available. Therefore, the Autoenrollment feature cannot work. In an Active Directory domain that has Microsoft Windows 2000 or later domain controllers, the problem may be caused by a DNS name resolution or by network connectivity issue.
Oppure legati al formato della richiesta come descritto nella KB312344 Request for Certificate Is Denied and a “The Request Subject Name Is Invalid or Too Long” Error Message Occurs:
This issue can occur if the subject in the Name box matches the name of the certification authority (CA).
The subject’s CN is string-compared and binary-compared to the issuer’s name. If the full DN names are available, these names are compared before a certificate is issued. Comparison does not depend on the actual encoding of the characters in the subject’s name.
Altri motivi potrebbero essere i seguenti:
Motivo 1: Problemi legati alla registrazione dei certificate templates in Active Directory come discusso nel post menzionato precedentemente Active Directory Domain Controllers and certificate auto-enrollment di Morgan Simonsen (MVP Enterprise Mobility), in questo caso è possibile tentare di registrare nuovamente i certificate templates tramite il comando:
certutil -SetCAtemplates +TemplateName
In alternativa è possibile tentare di registrare nuovamente tutti i templates tramite il comando (a riguardo si veda anche il post How to re-install the default certificate templates?):
certutil –InstallDefaultTemplates
Motivo 2: Problemi intercorsi durante la migrazione della CA, se da esempio la CA era una Standalone, ma per errore durante la procedura di migrazione la nuova CA è stata installata come Enterprise e poi è stato eseguito il ripristino delle chiavi di registro della precedente CA.
Per avere maggiori informazioni circa eventuali problemi legati autoenrollment dei certificati del Domain Controller è possibile abilitare su quest’ultimi l’enhanced logging del processo di auto-enrollment creando le seguenti chiavi di registro per avere eventi più dettagliati nel registro di log Application:
- Per abilitare l’enhanced logging dello User Auto-enrollment creare nella chiave HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Cryptography\Autoenrollment il valore AEEventLogLevel di tipo DWORD impostandolo a 0
- Per abilitare l’enhanced logging del Machine Auto-enrollment creare nella chiave HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Cryptography\Autoenrollment il valore AEEventLogLevel di tipo DWORD impostandolo a 0
Motivo 3: Problemi correlati alla registrazione in Active Directory della CA, per maggiori informazioni si veda il post Moving Your Organization from a Single Microsoft CA to a Microsoft Recommended PKI in cui viene anche chiarito che è anche possibile avere più Root CA nella propria foresta AD:
To be clear, there is absolutely no issue with installing multiple Windows root CAs in the same forest. You can deploy your new PKI and keep it from issuing certificates to your users or computers until you are good and ready for it to do so. And while you’re doing all this, the old CA will continue to chug along oblivious to the fact that it will soon be removed with extreme prejudice.
Each Windows CA you install requires some objects created for it in Active Directory. If the CA is installed on a domain member these objects are created automatically. If, on the other hand, you install the CA on a workgroup computer that is disconnected from the network, you’ll have to create these objects yourself.
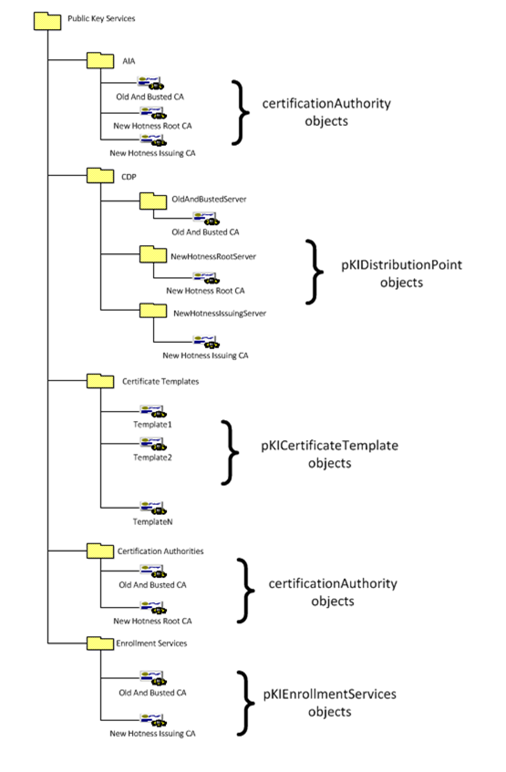
Di seguito i container e oggetti contenuti nel container CN=Public Key Services, CN=Services, CN=Configuration, DC=<forestRootPartition> memorizzati nella partizione Configuratione di AD in cui risiedono le registrazioni relative alla CA (si veda sempre il post Moving Your Organization from a Single Microsoft CA to a Microsoft Recommended PKI per maggiori dettagli):
Per verificare che la ricerca della CA nella propria infrastruttura avvenga correttamente è possibile eseguire il comando:
certutil -config – -ping
Per forzare sui Domain Controller l’esecuzione dell’Autoenrollment è possibile usare il comando:
certutil –pulse
Per ulteriori informazioni si vedano i seguenti:
- Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) Introduction
- Troubleshooting Autoenrollment
- How to troubleshoot Certificate Enrollment in the MMC Certificate Snap-in
- AD CS Upgrade and Migration Guide for Windows Server 2008 – Planning the Upgrade or Migration
- Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 – What’s New in Certificate Services in Windows Server