I vantaggi del UEFI
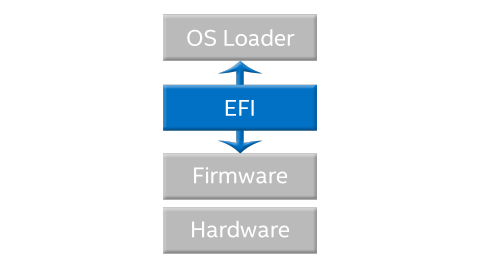 L’UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) è un’interfaccia firmware standard per PC creata da oltre 140 aziende aderenti al consorzio UEFI, tra cui Microsoft, per migliorare l’interoperabilità del software e risolvere le limitazioni del BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
L’UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) è un’interfaccia firmware standard per PC creata da oltre 140 aziende aderenti al consorzio UEFI, tra cui Microsoft, per migliorare l’interoperabilità del software e risolvere le limitazioni del BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
Di seguito i principali vantaggi del firmware UEFI:
- Miglioramento della sicurezza grazie alla protezione del processo pre-startup o pre-boot da attacchi di tipo bootkit.
- Maggiore velocità dei tempi di avvio e di ripresa dallo stato di ibernazione.
- Supporto agli hard disk di dimensioni maggiori di 2,2 terabyte (TB).
- Supporto di driver di dispositivi firmware a 64 bit che il sistema può utilizzare per indirizzare più di 17,2 miliardi di gigabyte (GB) di memoria durante l’avvio.
- Possibilità di utilizzare il BIOS con hardware UEFI.
- Supporto per il multicast deployment
Per maggiori informazioni si vedano:
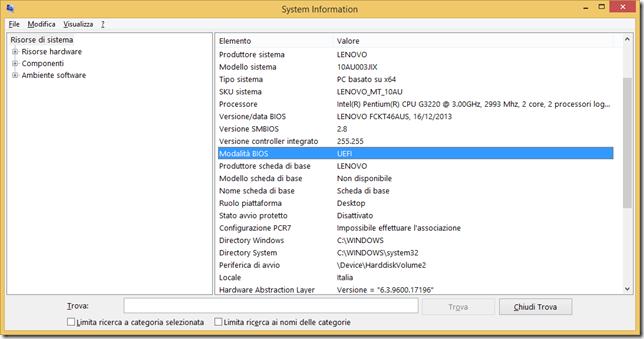
E’ possibile controllare se Windows è installato su un computer che utilizza UEFI oppure BIOS tramite il tool MSINFO32 ( a riguardo si veda How to check in Windows if you are using UEFI):
In alternativa è possibile utilizzare il cmdlet Confirm-SecureBootUEFI disponibile in WS2012/W8 e successivi per controllare se il computer utilizza UEFI e supporta il Secure Boot (a riguardo si veda il mio precedente post Secure Boot):
- If the computer supports Secure Boot and Secure Boot is enabled, then this cmdlet returns True.
- If the computer supports Secure Boot and Secure Boot is disabled, then this cmdlet returns False.
- If the computer does not support Secure Boot or is a BIOS (non-UEFI) computer, then this cmdlet returns an error displaying the following: Cmdlet not supported on this platform.
If Windows PowerShell® is not run in administrator mode, then this cmdlet returns an error displaying the following: Unable to set proper privileges. Access was denied.
This cmdlet requires that Windows PowerShell be run in administrator mode.
Per ulteriori approcci per controllare se se il computer utilizza UEFI si veda lo script PowerShell pubblicato al seguente Determine UEFI or Legacy BIOS from PowerShell (Three methods).
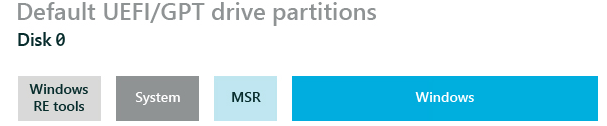
Quando Windows viene installato in computer che utilizzano UEFI anche la struttura delle partizioni di sistema di default cambiano come indicato nel seguente Configure UEFI/GPT-Based Hard Drive Partitions, di seguito la struttura di default:
Dove la partizione Windows RE tools è quella dedicata ai Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) Tools.
La configurazione raccomandata include anche una partizione per il recovery dell’immagine di sistema che conterà la Windows recovery image (install.wim) ed è raccomandabile che sia di almeno 3 GB:
Si noti che come indicato Configure UEFI/GPT-Based Hard Drive Partitions è importante che la partizione Recovery image sia posizionata al fondo del disco:
“Add the Windows RE Tools partition and system partition before you add the Windows partition. Add the partition that contains the recovery image at the end. This partition order helps keep the system and the Windows RE Tools partition safe during actions such as removing the recovery image partition or changing the size of the Windows partition.”
Per maggiori informazioni si vedano anche:


Vorrei sapere peró ,se si aggiorna il bios della scheda madre si hanno dei problemi circa la convalida di attivazione del sistema operativo,o sbaglio ? Esperienza personale….
Ci sono stai alcuni issu e causati da alcune implementazioni di UEFI a riguardo vedi:
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2962824
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2871690
e il thread http://www.bleepingcomputer.com/forums/t/526163/uefi-secure-boot-may-cause-windows-updates-to-fail-with-error-code-0x800f0922/